A guide for L&D professionals
Organizations must master a series of “ascents” in today’s rapidly changing global business market. These include upskilling, reskilling and improving employee performance. Yet, one fundamental idea that learning and development (L&D) professionals continues to ignore when designing new learning strategies is the learning curve. For them, understanding concepts is more than just theoretical knowledge. This affects virtually everything, including how training is designed, training duration, expected level of performance, and return on investment for specific activities. As companies increasingly demand top-class training, the need to thoroughly understand the learning curve has become a strategic imperative.
This article takes a closer look at the concept of the learning curve, what it means for employee development, and how L&D leaders can use it to maximize employee potential while saving training time and increasing the number of employees trained and skilled.
In this guide…
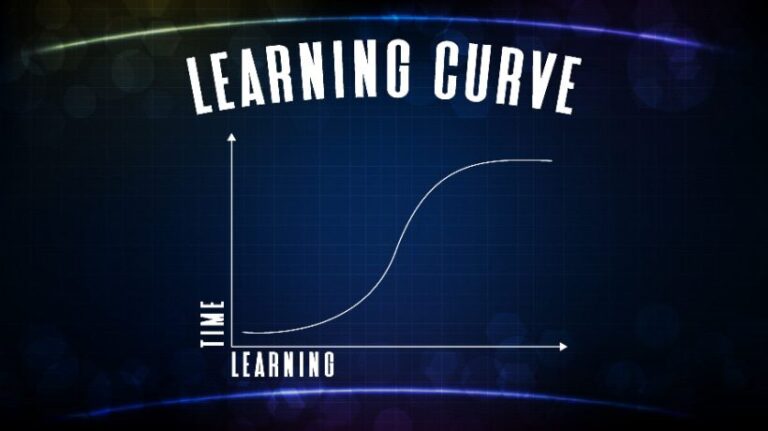
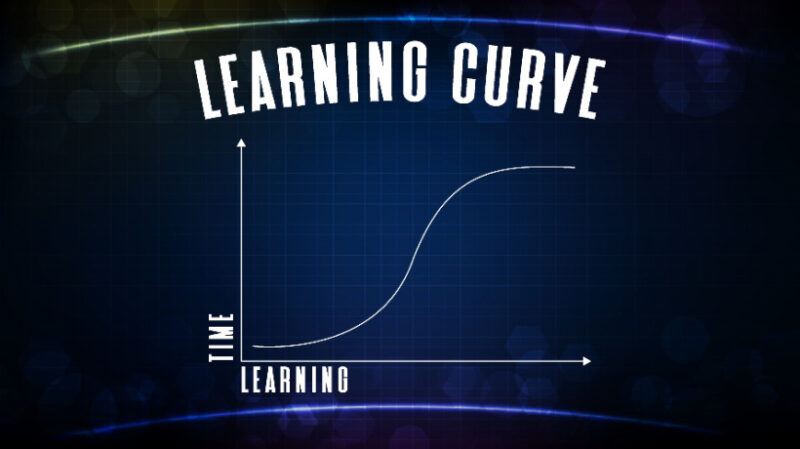
What is the learning curve?
A learning curve is a graph that shows the rate at which learners acquire new knowledge, skills, or abilities over time. Demonstrates gradual improvement in proficiency through repeated exposure and practice. Corporate training with learning curves will help you:
The period of time required for learners to reach competency. Level of steepness of learning progression. How to design training for faster learning.
Learning curves were first studied by psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus in the early 20th century. Since then, this concept has become integral to productivity research. Today’s L&D teams are tailoring training based on learning curves to reduce time to proficiency, reduce performance degradation, and improve knowledge retention.
Why learning curves matter for enterprise L&D
1. Reduce training time and help you achieve your desired results faster
A precisely managed learning curve helps predict “time to proficiency.” As an example, the 2023 Training Industry Report shows that organizations waste up to 25% of training time due to a disconnect between learning advancements and employees. When L&D teams bring learning curve insights into instructional design, they can not only adjust training length, but also speed for best results.
2. Supports resource allocation planning
Teams that recognize performance degradation during the learning curve also know how to effectively allocate support structures such as coaching, reinforcement tools, and just-in-time learning. One way companies can use analytics is to thoroughly map learner performance at different stages of the curve, making resource planning easier.
3. Realistic expectations for managers
One of the big issues that corporate L&D is dealing with is misaligned expectations. Managers typically expect performance to improve immediately after training, so they ignore the natural progression that learners must experience. Being comfortable with the learning curve allows leaders to set realistic goals, making talent conversations easier to manage and less stressful.
4. Upgrade your training ROI
Analyzing when learners are struggling, stagnating, or accelerating gives L&D professionals the opportunity to make modules more interesting, engaging, and more likely to stick. One of McKinsey’s findings states that companies that adopt a data-driven learning design approach can improve training effectiveness by 30-40%, which may be interpreted as a direct result of mastering the learning curve.
Different learning curves and their impact on companies
Knowledge of differences in learning curves can help L&D departments devise appropriate interventions.
1. Increased revenue (steep learning curve)
Learners pick up new skills very quickly during the early stages of a steep learning curve. Below is a perfect example.
Microlearning-based modules Gamification-enhanced learning experiences Simple procedural tasks
Using microlearning and simulation-driven techniques, an intentionally steep learning curve is created to quickly acquire skills.
2. Diminishing returns
In this case, the learner progresses very quickly at first. However, it gradually experienced a slowdown. This kind of learning curve is often seen in the following cases:
Leadership development Complex technical training Behavior change programs
These types of programs should provide reinforcement, coaching, and spaced learning to address plateaus.
3. S-curve
The learning curve shown here shows slow progress at first, rapid improvement in the middle, and stabilization at the end. The most frequently linked are:
Digital Transformation Training Software Onboarding Cross Functional Skills
Knowing about the S-shaped learning curve gives L&D professionals a hint that the training plan is long-term and gradually increases in difficulty.
Causes of learning curve in corporate training
1. Quality of instructional design
A well-thought-out plan, interesting and useful topics, and an engaging format all promote understanding of the content. A less-than-ideal training design will only make the curve steeper than it needs to be.
2. Learn how to serve
Blended learning, virtual instructor-led training, microlearning, and scenario-based learning methods each impact the curve differently. For example, microlearning has been proven to have a 22% positive effect on memory retention, according to the Journal of Applied Psychology.
3. Learner motivation
Motivation is the main factor that determines how quickly a person progresses through the learning curve. Incentives like recognition programs, gamification, and rewards can be very helpful in maintaining momentum.
4. Organizational learning culture
A supportive culture, which means, among other things, the provision of the necessary resources, coaching and practice opportunities, will undoubtedly lower the resistance factors and therefore make the learning curve more gradual.
5. Technology and AI
Using modern learning analytics, L&D leaders gain insights into learner performance and take the right actions at the right time to ease the curve.
How L&D professionals take advantage of the learning curve
1. Use learning analytics to discover bottlenecks
Studying learner behavior can be very helpful in understanding where specific individuals are struggling. Quick interventions in the form of nudges, microlearning boosters, or coaching can have a big impact on shortening the learning curve.
2. Make it easier to repeat by spacing out
According to the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve, without follow-up, learners forget almost 70% of new knowledge within 24 hours. Learning curves and spaced repetitions result in more durable memories.
3. Simplify complex skills
The “chunking” technique greatly reduces the learning difficulty, especially when dealing with S-curves and diminishing returns curves. This is a way to ensure that learners understand the basic concepts before moving on to the next step.
4. Incorporate practice and application
When employees practice with real-life scenarios, their learning rate increases significantly. For example, simulators, role-playing, and AR/VR setups are some of the ways to reduce fear of failure and increase confidence.
5. Introduce microlearning to enhance learning
Short, easy-to-understand modules are a great way to enhance your content because they deliver content at the right time.
6. Set realistic competency goals
L&D staff would be better off if they devised a milestone-based system for tracking progress, rather than just expecting human learning to be strictly linear. This practice is consistent with real human learning patterns.
7. Benefit from social and collaborative learning
Research groups, communities of practice, and peer learning all have a curve-flattening effect because they foster shared problem-solving and knowledge exchange.
Learning curve and current L&D trends
Innovative training technologies have changed the way organizations perceive learning curves.
AI-powered learning path
Artificial intelligence analyzes learner behavior and creates a tailored training path for each employee based on that. Therefore, the learning curve is optimized only for the individual.
Learning Experience Platform (LXP)
LXP helps learners overcome plateaus by smartly retrieving personalized content that is more likely to interest and benefit them.
Simulation-based learning
Simulations can help shorten skill-based learning curves because they provide a risk-free practice environment.
Microlearning at scale
Microlearning is one of the key strategies used to ensure faster progress at the beginning of the learning curve.
conclusion
For L&D professionals, understanding the learning curve is essential to creating training programs that are not only time-efficient, but also learner-centered and performance-driven. The questions of how quickly employees can learn and what methods are most effective for them have never been more important than they are now. When combined with modern instructional design, data analytics, and cutting-edge learning solutions, the learning curve becomes a strategic vehicle for workforce transformation.
Ultimately, understanding the learning curve gives organizations the opportunity to set realistic expectations, improve training outcomes, reduce time to competency, and build a strong learning culture that constantly changes and evolves to meet business requirements.